Blog •
Last updated on Apr 17, 2024
What is a Vanity Press? A Guide to Vanity Publishing
About the author
Reedsy's editorial team is a diverse group of industry experts devoted to helping authors write and publish beautiful books.
More about the Reedsy Editorial Team →Martin Cavannagh
Head of Content at Reedsy, Martin has spent over eight years helping writers turn their ambitions into reality. As a voice in the indie publishing space, he has written for a number of outlets and spoken at conferences, including the 2024 Writers Summit at the London Book Fair.
View profile →Put simply, a vanity press is a publisher that profits not from selling books but from asking authors to pay for publishing expenses. Of course, there are a lot more nuances, and this definition makes it easy to mistake legitimate companies for the unscrupulous ones.
In this post, we’ll go over vanity presses with a magnifying glass to pinpoint their mechanism and defining features. For the quick version, here’s an infographic on the differences between a traditional publisher and a vanity press.
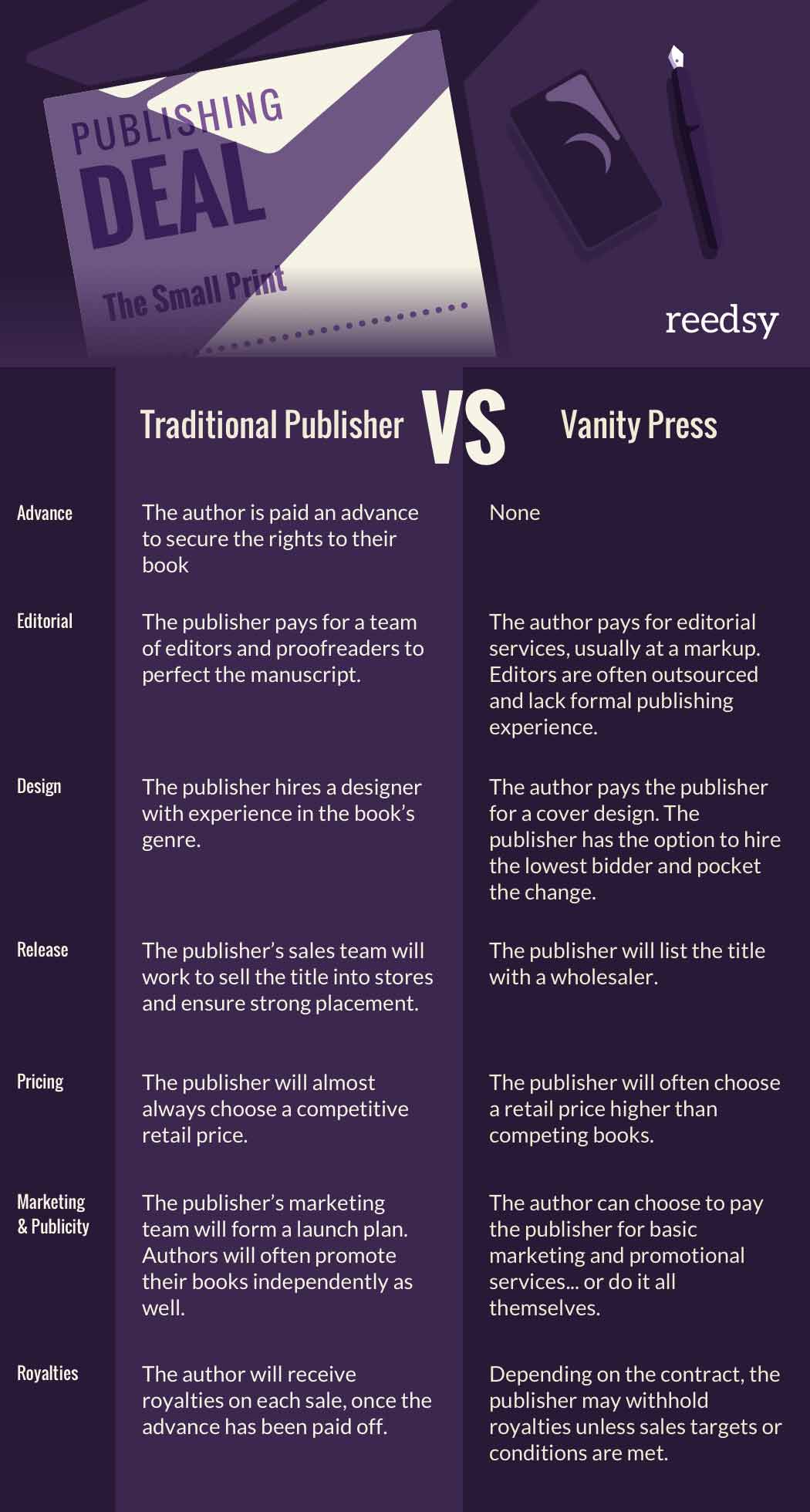
The author pays to publish
The traditional model of publishing is like this:
- The author submits their manuscript to a publisher.
- The publisher reads and decides whether to acquire the manuscript.
- Once there is an acquisition, the publisher gives the author an advance (usually in the thousands of dollars).
- The publisher’s editors and designers work to get it ready for readers’ eyes.
- The publisher takes care of printing, distribution to bookstores and libraries, gaining publicity through book reviews, store displays, advertisements, and events.
- When the book sells, the author gets between 7% to 25% royalty (depending on the format) of the net sales price after the advance has been covered.
At no point in this process does the author pay the publisher. This is because traditional publishers aren’t service providers — they are producers of books. They buy the rights to publish and sell an author’s creation, and they will take on the financial risk associated with this.
Vanity presses don’t follow this model. They tend not to be selective in terms of which book they publish, because what matters to them isn’t the quality of the book or how it appeals to readers. Their income stream doesn’t come from selling books — it comes from selling authors on the dream of seeing their book in print.
They’ll ask authors to pay for production costs, including editing and designing fees. There is little to no transparency about what these expenses entail, and whether they align with industry standards. So a vanity press may say you’re only footing 20% of the bill when, in fact, you're giving them far more than that. And after that, they’ll still keep a massive chunk of any sales you make — just as a traditional publisher might.
No quality service to accompany the cost
Despite asking you to pay for editing and designing, more often than not, the services that your book will get will be subpar. Since quality doesn’t matter to vanity publishers, and they want to save on costs, they’ll be happy to use inexperienced workers and ready-made templates for the sake of ticking tasks off the production to-do list.
Q: How can authors spot red flags when approached by a vanity press?
Suggested answer
Spotting the red flags when dealing with a vanity press can save you a lot of headaches (and money!). Here are some key things to watch for:
- Upfront Fees: If they’re asking you to shell out big bucks to publish your work, it’s a major red flag. Legitimate publishers make money from selling books, not charging authors.
- Unrealistic Promises: Claims like “guaranteed bestseller” or “we’ll get you into every bookstore!” are major eye-roll territory. No one can promise that, and reputable publishers won’t even try.
- Accepting Anything: A real publisher is picky—they have to be since they invest in what they publish. If a press will take your book with zero hesitation (and no editing), chances are it’s more about your money than your talent.
- Vague Contracts or none at all: If the contract feels murky, confusing, or doesn’t make it clear what you’re getting and what rights you retain, that’s a huge red flag. Always know what you’re signing!
- Hidden Costs: Watch for surprise fees for “marketing,” “editing,” or “special services.” It’s a tactic used to squeeze more out of you once you’re already on the hook.
- Pushy Sales Tactics: If they’re coming at you hard with “limited-time offers” or pressuring you to sign fast, it’s a no-go. Legit publishers won’t need to convince you that hard.
- Shady Reputation: Do a quick online search. If you see lots of unhappy authors and stories of people feeling scammed, run the other way.
- Limited Distribution Claims: Be wary if their “distribution network” is mostly online listings without meaningful reach or promotion. Real publishers have genuine connections in the industry and established distribution channels.
- No Editing or Quality Control: If there’s no real editorial process or constructive input, it indicates they don’t care about the quality of your work—just about getting paid.
Bottom line is if it feels off or you’re seeing a bunch of these warning signs, trust your gut and dig deeper. Your work deserves better!
Eilidh is available to hire on Reedsy ⏺
I think we need to first distinguish between vanity presses and hybrid/independent publishers. There are legitimate publishers with a business model that includes an upfront payment from authors. This payment funds the production of the book, and then includes a royalty split in favor of the author, such as 70/30 or even 80/20.
Those are hybrid presses, which help keep much of the decision-making surrounding the book in the author's hands and provide a means for authors to benefit the most if the book sells well. They don't accept every book they are pitched, have quality standards that rival traditional publishers, and make money when more books are sold.
The hybrid model is different from a vanity press, which earns the bulk of its money from the pre-production and printing costs. Vanity presses rarely turn any author down who can pay for its services. Printing and design quality varies but you can still get a good-looking book from a vanity press, it will just be very expensive.
To know if you're dealing with a vanity press or a hybrid/independent press look for:
- Writers guidelines. Do they have any guidelines or will they publish anything?
- A sense of urgency. Vanity presses want to get you to commit and pay them money. This may lead to frequent emails, texts, and phone calls to inquire about the hold-up.
- Distribution details. Once your book is printed, how will the publisher get it into bookstores and, ultimately, readers? They should have a distribution partner, such as Simon & Schuster.
In addition to vanity presses, there are many, many scam operations that have cropped up offering to ghostwrite and publish your book for a couple thousand dollars. Be aware that you will likely get nothing, or next to nothing. Avoid these at all costs.
Scammers may have a legit-sounding company name but will lack any information about the founders and the team members who will be doing the work. They will feature gorgeous cover photos of books they never had anything do with producing, but which look impressive. They will feature "testimonials" and A+ Better Business Bureau (BBB) and TrustPilot ratings that are fake - type in the BBB and TrustPilot URLs yourself to check for the real reviews. And they, too, will hound you to sign on the dotted line and send them money.
If the deal being offered sounds too good to be true, it very likely is. Protect yourself.
But the reality is that few first-time authors will qualify for a traditional publishing deal that doesn't involve paying for production. This is because the Big 5 publishers are risk averse and want book deals from people who have huge platforms and social media follower counts. That is, they want to be almost assured that your book will be a bestseller, and few authors can guarantee that. Which is why hybrid publishing is a terrific alternative.
Marcia is available to hire on Reedsy ⏺
The easiest way to distinguish a scam publisher from a reputable hybrid publisher or self-publisher is PRICE. If a publishing firm quotes a fee of just a few thousand dollars for a service package that includes everything from copy editing, cover design, and layout to marketing and publicity—or even ghostwriting and developmental editing—you’re probably dealing with scammers. I know this from experience and from the fact that any single one of those services, when delivered by skilled and experienced professionals, usually costs more than a few thousand dollars. By contrast, the fees charged by the reputable hybrid publishers I know—companies with a track record of obtaining meaningful results for their authors—start in the $15,000 range. Several of my past clients made the mistake of opting for cut-rate vanity presses, and all of them came to regret it. When you hire a publisher that charges cut rates, you get cut-rate services in return.
Peter is available to hire on Reedsy ⏺
The fact that they're a vanity press is the only red flag you need. 😉 Seriously, though, I'd aim for either traditional publishing or full-on self-publishing. These companies who want you to go in on the costs are generally more trouble than they're worth. Caveat emptor.
Brett is available to hire on Reedsy ⏺
The publisher still profits if your book doesn’t sell
Vanity presses require payment for editing, designing, and marketing services because this is how they make money. Much like the unscrupulous Broadway impresarios Bialystock & Bloom from Mel Brooks’ The Producers, they don’t care about the commercial success of your book because they’ve already acquired revenue directly from you.

So, even if your book doesn’t sell, a vanity publisher will still make a profit. In fact, they may even earn more money, since they can tell you to invest in one of their marketing packages. Sales, editorial quality, current market trends — none of that interests a vanity publisher.
This is why, if you dive into their book catalog, you’ll likely find that no single title makes the bestseller lists on Amazon for more than a day. Many of their books won't have a lot of customer reviews on them either since there are hardly any readers.
'Distribution to major bookstores' isn’t what it sounds like
Though a common promise, distribution to major bookstores isn’t as easy to achieve as it sounds. Traditional publishers have sales representatives with the negotiation skills, reputation, and connections needed to get your book to big chains; the same can’t be said for vanity presses.
Instead, they will probably list your book on a distribution service like Ingram. This listing allows a range of brick-and-mortar shops to order your book, but it doesn’t guarantee actual orders. Whether you get your book into stores depends on the ties you can establish with booksellers and readers. If many readers ask for your book at an independent bookshop, the seller will likely order the title in.
From the Big 5 to small boutique presses, every reputable publisher has a team with ties with booksellers. A vanity press won’t. They’ll list your book (which you can easily do yourself) and leave the rest to you while making you pay through the nose.
They may own your printing rights for years to come
As mentioned before, when a publisher acquires your book, they buy the rights to publish and sell it. You, the author, can negotiate how extensive the publisher’s rights will be and how long they get to keep them.
For instance, you may give an American-based publisher first publishing rights, meaning they get to be the first to have a print run for your book in the USA. You may keep the reprint rights to decide whether to continue working with this publisher or not in the future. Foreign publishing rights can be sold to another publisher that is better suited for the job. This way, you always get to control who publishes your book.
However, a scammer may try to wrestle this control from your hands. Approaching authors who aren't represented by an agent (or are unaware of these legalities), scammers may nestle a term in the contract that gives them the exclusive rights to publish, reprint, and even sell the rights for future editions of your book to other publishers. This allows them to trade your creation while cutting you out of the process altogether.
A vanity press like this can be quite difficult to distinguish, and the scamming occurs via technical details in legal documents that will likely overwhelm any author. This is why it is crucial to find a reliable agent when planning to publish traditionally. Good agents are experienced in this line of work and can help you suss out fine-print details on a contract, negotiating them to benefit you.
Q: How can authors spot red flags when approached by a vanity press?
Suggested answer
Spotting the red flags when dealing with a vanity press can save you a lot of headaches (and money!). Here are some key things to watch for:
- Upfront Fees: If they’re asking you to shell out big bucks to publish your work, it’s a major red flag. Legitimate publishers make money from selling books, not charging authors.
- Unrealistic Promises: Claims like “guaranteed bestseller” or “we’ll get you into every bookstore!” are major eye-roll territory. No one can promise that, and reputable publishers won’t even try.
- Accepting Anything: A real publisher is picky—they have to be since they invest in what they publish. If a press will take your book with zero hesitation (and no editing), chances are it’s more about your money than your talent.
- Vague Contracts or none at all: If the contract feels murky, confusing, or doesn’t make it clear what you’re getting and what rights you retain, that’s a huge red flag. Always know what you’re signing!
- Hidden Costs: Watch for surprise fees for “marketing,” “editing,” or “special services.” It’s a tactic used to squeeze more out of you once you’re already on the hook.
- Pushy Sales Tactics: If they’re coming at you hard with “limited-time offers” or pressuring you to sign fast, it’s a no-go. Legit publishers won’t need to convince you that hard.
- Shady Reputation: Do a quick online search. If you see lots of unhappy authors and stories of people feeling scammed, run the other way.
- Limited Distribution Claims: Be wary if their “distribution network” is mostly online listings without meaningful reach or promotion. Real publishers have genuine connections in the industry and established distribution channels.
- No Editing or Quality Control: If there’s no real editorial process or constructive input, it indicates they don’t care about the quality of your work—just about getting paid.
Bottom line is if it feels off or you’re seeing a bunch of these warning signs, trust your gut and dig deeper. Your work deserves better!
Eilidh is available to hire on Reedsy ⏺
I think we need to first distinguish between vanity presses and hybrid/independent publishers. There are legitimate publishers with a business model that includes an upfront payment from authors. This payment funds the production of the book, and then includes a royalty split in favor of the author, such as 70/30 or even 80/20.
Those are hybrid presses, which help keep much of the decision-making surrounding the book in the author's hands and provide a means for authors to benefit the most if the book sells well. They don't accept every book they are pitched, have quality standards that rival traditional publishers, and make money when more books are sold.
The hybrid model is different from a vanity press, which earns the bulk of its money from the pre-production and printing costs. Vanity presses rarely turn any author down who can pay for its services. Printing and design quality varies but you can still get a good-looking book from a vanity press, it will just be very expensive.
To know if you're dealing with a vanity press or a hybrid/independent press look for:
- Writers guidelines. Do they have any guidelines or will they publish anything?
- A sense of urgency. Vanity presses want to get you to commit and pay them money. This may lead to frequent emails, texts, and phone calls to inquire about the hold-up.
- Distribution details. Once your book is printed, how will the publisher get it into bookstores and, ultimately, readers? They should have a distribution partner, such as Simon & Schuster.
In addition to vanity presses, there are many, many scam operations that have cropped up offering to ghostwrite and publish your book for a couple thousand dollars. Be aware that you will likely get nothing, or next to nothing. Avoid these at all costs.
Scammers may have a legit-sounding company name but will lack any information about the founders and the team members who will be doing the work. They will feature gorgeous cover photos of books they never had anything do with producing, but which look impressive. They will feature "testimonials" and A+ Better Business Bureau (BBB) and TrustPilot ratings that are fake - type in the BBB and TrustPilot URLs yourself to check for the real reviews. And they, too, will hound you to sign on the dotted line and send them money.
If the deal being offered sounds too good to be true, it very likely is. Protect yourself.
But the reality is that few first-time authors will qualify for a traditional publishing deal that doesn't involve paying for production. This is because the Big 5 publishers are risk averse and want book deals from people who have huge platforms and social media follower counts. That is, they want to be almost assured that your book will be a bestseller, and few authors can guarantee that. Which is why hybrid publishing is a terrific alternative.
Marcia is available to hire on Reedsy ⏺
The easiest way to distinguish a scam publisher from a reputable hybrid publisher or self-publisher is PRICE. If a publishing firm quotes a fee of just a few thousand dollars for a service package that includes everything from copy editing, cover design, and layout to marketing and publicity—or even ghostwriting and developmental editing—you’re probably dealing with scammers. I know this from experience and from the fact that any single one of those services, when delivered by skilled and experienced professionals, usually costs more than a few thousand dollars. By contrast, the fees charged by the reputable hybrid publishers I know—companies with a track record of obtaining meaningful results for their authors—start in the $15,000 range. Several of my past clients made the mistake of opting for cut-rate vanity presses, and all of them came to regret it. When you hire a publisher that charges cut rates, you get cut-rate services in return.
Peter is available to hire on Reedsy ⏺
The fact that they're a vanity press is the only red flag you need. 😉 Seriously, though, I'd aim for either traditional publishing or full-on self-publishing. These companies who want you to go in on the costs are generally more trouble than they're worth. Caveat emptor.
Brett is available to hire on Reedsy ⏺
Generally, a red flag is when anyone approaches you and asks for funds upfront. This can be an agent or publisher. In general, legitimate agents and publishers have enough people approaching them without them having to pound the pavement to look for authors.
Attending writing conferences is one of the best ways to interact with legitimate agents and publishers. This is where they try to connect with authors directly and will not ask for money from the author.
Melody is available to hire on Reedsy ⏺
Most “hybrid publishers” are actually vanity presses
 Now, to complicate matters a little, there are publishers out there who charge fees for editing, designing, and marketing the book but are also invested in its commercial success rather than profit from the fees collected alone. These are legitimate hybrid publishers, but telling them apart in a sea of vanity presses can be difficult.
Now, to complicate matters a little, there are publishers out there who charge fees for editing, designing, and marketing the book but are also invested in its commercial success rather than profit from the fees collected alone. These are legitimate hybrid publishers, but telling them apart in a sea of vanity presses can be difficult.
As a rule of thumb, you should immediately be wary when you see the “hybrid publisher” label. Be sure to research the company carefully — we have a guide to hybrid publishing here to help you stay vigilant.
Know also that the hybrid publishing model, though it isn’t outright predatory, means that you will have to shoulder much of the financial risks of putting your book out there. A hybrid publisher doesn’t have the resources a traditional publisher has, and those limited resources must be shared between several authors. Hybrid publishers may not be able to provide you with the best, most tailored services to help you reach your target audience.
If you don’t publish with a traditional publisher, it may be safer to collaborate with qualified professional editors, cover designers, and marketers with experience in your niche to self-publish your book. They will be able to dedicate time and effort to your project and give you the best chance of success.

MEET THE BEST PUBLISHING PROFESSIONALS
Polish your book with expert help
Sign up to browse 2000+ experienced editors, designers, and marketers.
Some vanity presses are associated with major publishers
To complicate things, some of the world's most prolific vanity presses are closely connected with major traditional publishers. Xlibris and Author Solutions (which we mentioned in our previous post on shady companies) were, at various points, owned by Pearson and Penguin Random House — both Big 5 presses.
While their business model is identical to all other vanity presses, these trad-adjacent vanities sometimes suggest to authors that working with them may gain the attention of their legitimate imprints.
Print titan Simon & Schuster also has a vanity publishing arm called Archway Publishing, which makes this suggestion explicit on their website:
Select titles published by Archway are reviewed by a board made up of Simon & Schuster editors for possible acquisition by Simon & Schuster.
Note that only a selection of books is reviewed for possible acquisition—without mentioning how often this board convenes and how many books are submitted to it.
If you are looking for a traditional publishing deal, landing an agent is significantly easier (and cheaper) than jumping through the hoops at a vanity press.
Hopefully, this post has helped you understand the ins and outs of vanity presses and made it easier for you to notice warning signs.

